Malaria, yellow fever, Zika virus, dengue fever, West Nile fever, Chikungunya … so many diseases and viruses that have exploded in recent years. Their common thread ? They are all transmitted by mosquitoes. Thus, in early 2015, Brazil experienced a 550% increase in the number of cases of dengue , a tropical fever that spreads through the bite of the tiger mosquito ! But why are diseases like Zika or certain insects now appearing ? What are its consequences and, above all, what projects and solutions should be proposed ?
The observation: mosquito alert, health in danger!
In the continental United States, almost all human diseases involving arthropods are a mixture of different types of encephalitis. These viruses attack the central nervous system and the effects of these infections vary in some people, from a benign disease, to death in others. In many cases, it causes irreversible damage to the central nervous system. Because it is better to know his “enemy” to better combat it, let us interest ourselves in these diseases that proliferate throughout the world .
The Zika virus
Highly publicized lately, this virus was first identified in 1947, in the Zika forest in Uganda. Similar to dengue fever and yellow fever , it first appeared in monkeys. Until 2007, Zika did not talk about him until an epidemic broke out on the Yap Islands of the Federated States of Micronesia, affecting about 8,000 people. Between 2013 and 2014, a new epidemic affects more than 8,000 people in French Polynesia and between 2014 and 2015, about 1.5 million people. In particular, the virus was spread from Polynesia to Brazil in mid-2014 during the World Cup.

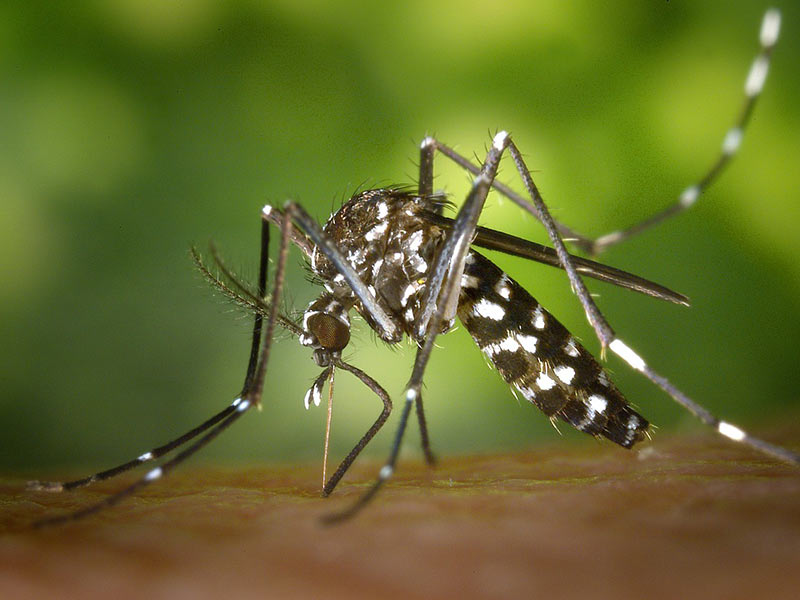
The tiger mosquito
Tiger mosquitoes are particularly active with the arrival of heat in May. They have chemical sensors on their antennas, but also visual sensors, odor and temperature sensors. This is why some people are more likely to be stung than others because they emit a greater amount of carbon dioxide through breathing or sweating. The tiger mosquito originated in Southeast Asia and reached Europe in the 1980s. It then spread rapidly, transported by sea in goods, over long distances. These mosquitoes are able to withstand very low temperatures. Today, if 51 French departments are concerned by the presence of the tiger mosquito, 30 are particularly in the red.
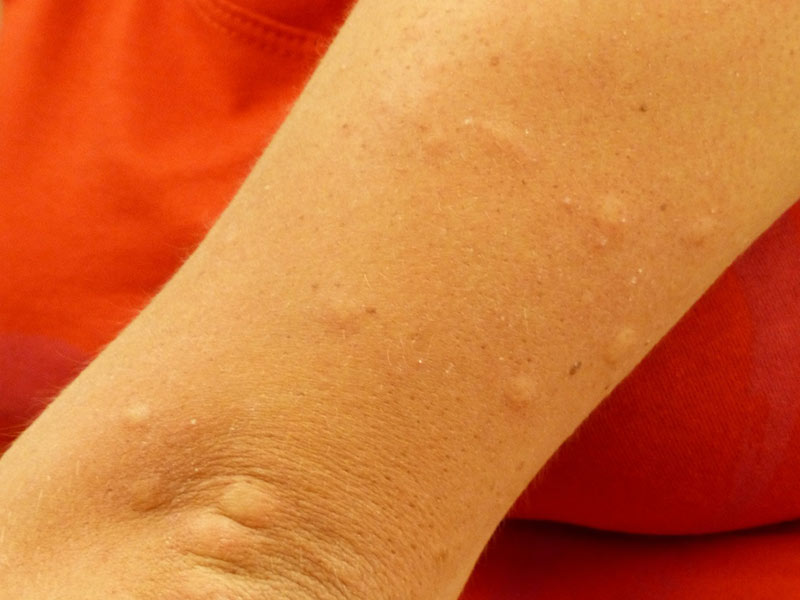
The dengue
The dengue is a viral disease transmitted by mosquitoes, which results in significant pain in joints and muscles, swollen glands and rashes on the skin. The mosquito Aedes aegypti sting the people at any time of day or night. Contagion occurs only if the mosquito is infected. Dengue is not transmitted directly from one person to another, through objects or breast milk. According to WHO, 390 million people are infected with dengue each year.
Malaria
The malaria is caused by protozoa of the genus Plasmodium. Characteristics of malaria transmission and disease vary across regions, within a country. It depends on the species of the parasite, environmental conditions and socio-economic factors such as poverty and conditions of access to care and prevention. In South Asia, resistance to malaria drugs is the highest in the world.
Chikungunya
Venezuela, Haïti, Guyana, Mexico … The chikungunya virus spreads throughout America and alarms the inhabitants. 2 mosquitoes in particular are the cause: the Aedes aegypti and the Aedes albopictus, the same ones that cause dengue fever and yellow fever . The transmission does not occur from person to person but it is the mosquito that transmits the virus during the bite.
The symptoms are very similar to those of dengue: intense pain in joints and muscles . It also produces a headache, vomiting and a high fever. Although chikungunya is not a deadly virus, it may slow the development of children, Weakened elderly or pregnant women and people with chronic illnesses.
Chikungunya was first identified in Tanzania 60 years ago. It has since expanded into Asia, Southern Europe with an epidemic in 2007 in Italy and southern France in 2010, and reached the Caribbean in 2013, with cases in Martinique.
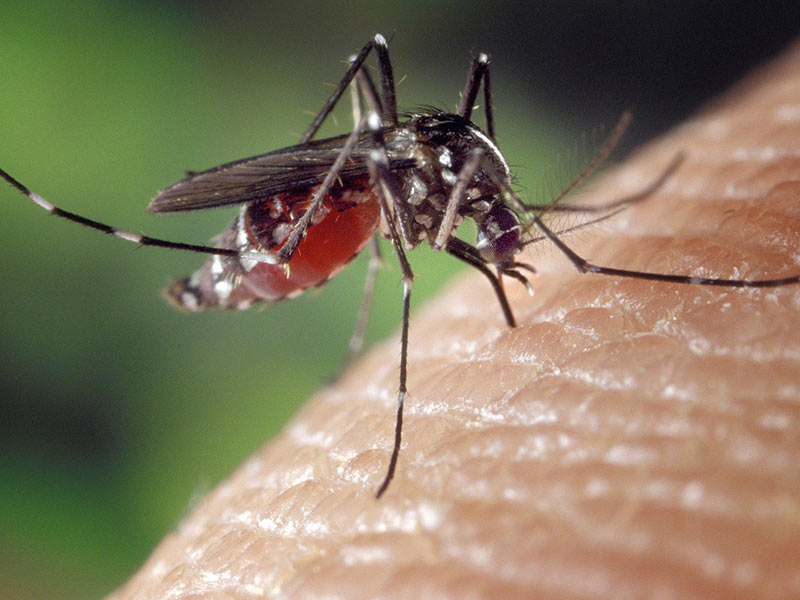
Yellow Fever
Contagion occurs only through the bite of infected mosquitoes. The first symptoms may be similar to those of the flu:
- fever
- headache
- vomiting
- muscle aches.
When the disease progresses, bleeding gums and blood in the urine appear. The patient may also suffer from jaundice.
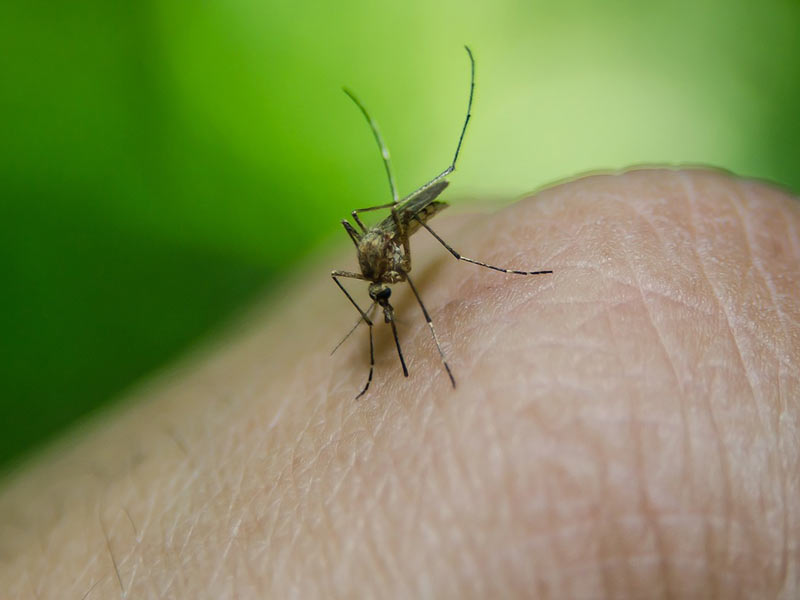

The projects and solutions of the OMPE: how to (really) tremble the mosquitoes?
Faced with the proliferation of patients suffering from the Zika virus or stung by the tiger mosquito, some authorities have put in place radical ideas. The OMPE has focused on these “solutions” that kill a multitude of insects, other animals and plants… and occasionally mosquitoes and ticks.
Stop chemical solutions to eradicate mosquitoes
What if we were not told everything? At a time when the Zika virus is causing the alarming development of newborn microcephaly in Latin America, a recent study shows that the true cause of this condition is due to a chemical : Pyriproxifene developed by Sumitomo Chemical, a company sponsored by Monsanto. Again… Introduced into waters 2 years ago, Pyriproxifene was intended to develop malformations in mosquitoes and thus slow down the progression of larvae in drinking water tanks.
But this product is not the only one to have been questioned. In 2016, beekeepers from South Carolina, discovered millions of bees dead on their farms. The cause : aerial spraying of the Naled insecticide, banned in 2012 by the European Union, to eliminate the mosquitoes carrying the Zika virus. This insecticide is also toxic to butterflies, fish and other aquatic organisms.

Slowing global warming, mosquito-friendly soil
The discussion on the health risks of climate change is more present than ever. The World Health Organization estimates that between 2030 and 2050, climate change will cause an additional 250,000 deaths each year due to malnutrition, thermal stress and malaria.
Indeed, weather conditions have a great influence on insect-borne diseases, especially malaria. These changes are likely to extend the stations of transmission of the main diseases generated and alter their geographical distribution.
Malaria , transmitted by mosquitoes of the genus Anopheles, kills nearly 600,000 people each year. Mosquitoes of the genus Aedes, vectors of dengue, are also very sensitive to weather conditions.

Slowing global warming, mosquito-friendly soil
The discussion on the health risks of climate change is more present than ever. The World Health Organization estimates that between 2030 and 2050, climate change will cause an additional 250,000 deaths each year due to malnutrition, thermal stress and malaria.
Indeed, weather conditions have a great influence on insect-borne diseases, especially malaria. These changes are likely to extend the stations of transmission of the main diseases generated and alter their geographical distribution.
Malaria , transmitted by mosquitoes of the genus Anopheles, kills nearly 600,000 people each year. Mosquitoes of the genus Aedes, vectors of dengue, are also very sensitive to weather conditions.

Leveraging innovative new technologies for massive mosquito control
In 2015, two French engineers invented a mosquito trap of a new kind: the mosquito vacuum cleaner. In the form of bollards, it attracts mosquitoes with a mixture of carbon dioxide and pheromones, identical to those of the human body, then sucks the insect when it approaches.
If these vacuum cleaners are currently only used on Camargue mosquitoes, they are promised a bright future, avoiding massive mosquito control by chemical substances.




